Ion-exchange Resin

An ion-exchange resin or ion-exchange polymer is a resin or polymer that acts as a medium for ion exchange. It is an insoluble matrix (or support structure) normally in the form of small (0.25–0.5 mm radius) micro beads, usually white or yellowish, fabricated from an organic polymer substrate. The beads are typically porous, providing a large surface area on and inside them. The trapping of ions occurs along with the accompanying release of other ions, and thus the process is called ion exchange. There are multiple types of ion-exchange resin. Most commercial resins are made of polystyrene sulfonate.
Ion-exchange resins are widely used in different separation, purification, and decontamination processes. The most common examples are water softening and water purification. In many cases ion-exchange resins were introduced in such processes as a more flexible alternative to the use of natural or artificial zeolites. Also, ion-exchange resins are highly effective in the bio diesel filtration process.
Anion resins and cation resins are the two most common resins used in the ion-exchange process. While anion resins attract negatively charged ions, cation resins attract positively charged ions.
Anion resins
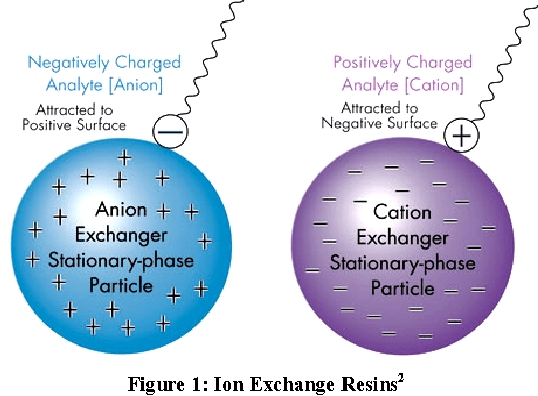
Anion resins may be either strongly or weakly basic. Strongly basic anion resins maintain their positive charge across a wide pH range, whereas weakly basic anion resins are neutralized at higher pH levels.Weakly basic resins do not maintain their charge at a high pH because they undergo deprotonation. They do, however, offer excellent mechanical and chemical stability. This, combined with a high rate of ion exchange, make weakly base anion resins well suited for the organic salts.
For anion resins, regeneration typically involves treatment of the resin with a strongly basic solution, e.g. aqueous sodium hydroxide. During regeneration, the regenerate chemical is passed through the resin, and trapped negative ions are flushed out, renewing the resin exchange capacity.
Cation-exchange resin

The cation exchange method removes the hardness of water but induces acidity in it, which is further removed in the next stage of treatment of water by passing this acidic water through an anion exchange process. Formula: R−H acidic.
Application
- Water softening
- Water purification
- Metal sepration
- Juice purification
- Sugar Manufacturing
- Pharmaceuticals
